Three years on, RCEP sees significant progress in promoting regional open cooperation
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is the free trade agreement with the largest participating population in the world, as well as the largest economic and trade scale, and the greatest development potential.
Since the RCEP came into force in January 2022, it has delivered increasingly prominent institutional dividends such as tariff reductions, simplified customs procedures, and trade and investment facilitation. It has played a crucial role in safeguarding the stability and smooth flow of regional industrial and supply chains, propelling the Asia-Pacific into a new period of high-quality economic development.
On the morning of Jan. 2, 2025, a freight train loaded with fresh fruits and vegetables set off from Wangjiaying West Station in Kunming, southwest China's Yunnan province, bound for Laos along the China-Laos Railway.
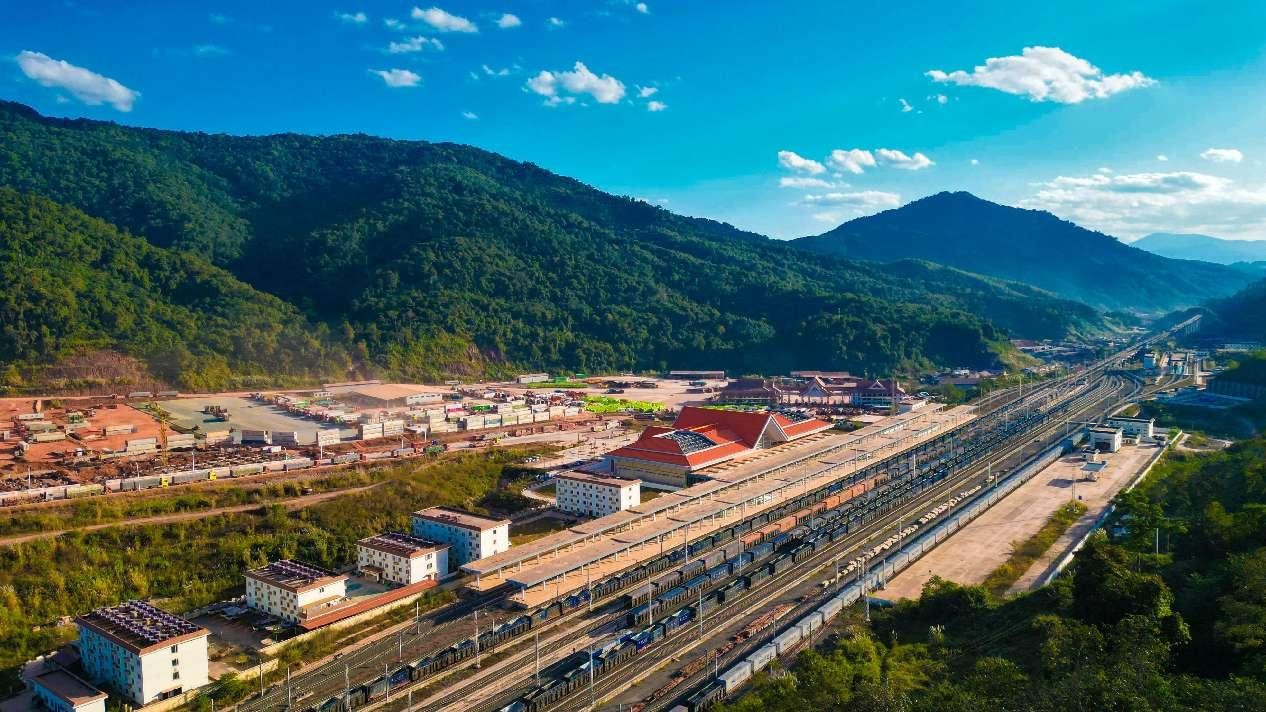

Photo shows the Boten Station of the China-Laos Railway in Luang Namtha, Laos. (Photo/Yang Yongquan)
This marked a new milestone for the railway, which has transported over 50 million tons of cargo, including 11.58 million tons of cross-border goods, since its full operation on Dec. 3, 2021.
Over the past three years since the RCEP came into force, the China-Laos Railway has emerged as a crucial transport corridor linking China, Thailand, Cambodia, and other countries. With the opening of more shipping routes, goods from Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, and Japan can now directly reach Xiamen Port and Quanzhou Port in southeast China's Fujian province, as well as ports in east China's Shandong province.
According to a study conducted by the Asian Development Bank, by 2030, the RCEP is expected to add $245 billion annually to regional income and 2.8 million jobs to regional employment. With the continuous improvement of regional connectivity, the RCEP will unleash more trade benefits.
Providing tremendous opportunities for regional enterprises
Boten town in northern Laos' Luang Namtha province, located only 3 kilometers from the Chinese border town of Mohan in Yunnan, is a crucial border station for transporting goods between China and Laos by land.
"Three years ago, there were only about a dozen customs clearance companies in Boten. Now, there are around 150," said Zhang Jianli, head of the freight transfer division at the Boten Station of the China-Laos Railway.
Inside the offices of these customs clearance companies, business agents were busy submitting documents, inspecting goods, and paying taxes to ensure timely shipment of goods for their customers.
Thanaleng Dry Port, a border checkpoint located between Lao capital Vientiane and border city Nong Khai in northeast Thailand, primarily handles goods that need to transit through Laos before reaching China or Thailand.
With the opening of the China-Laos Railway, the time needed to transport goods from Vientiane to Boten has reduced from two days by trucks to only around four hours, enhancing the logistics efficiency in the region.
By implementing tariff commitments, rules of origin, trade and investment liberalization and facilitation, and other trade regulations, the RCEP has maximized the integration of 27 trade arrangements and 44 investment agreements of its members in the region. This has effectively advanced the development of the multilateral trading system and helped maintain the stability of industrial and supply chains across the region.
An executive from the United Overseas Bank in Singapore said that the RCEP has broken down tariff barriers among its members and simplified trade rules. Singaporean enterprises can enjoy an average of 92 percent tariff reduction in China, which provides them with more favorable conditions for expanding their presence in the Chinese market.
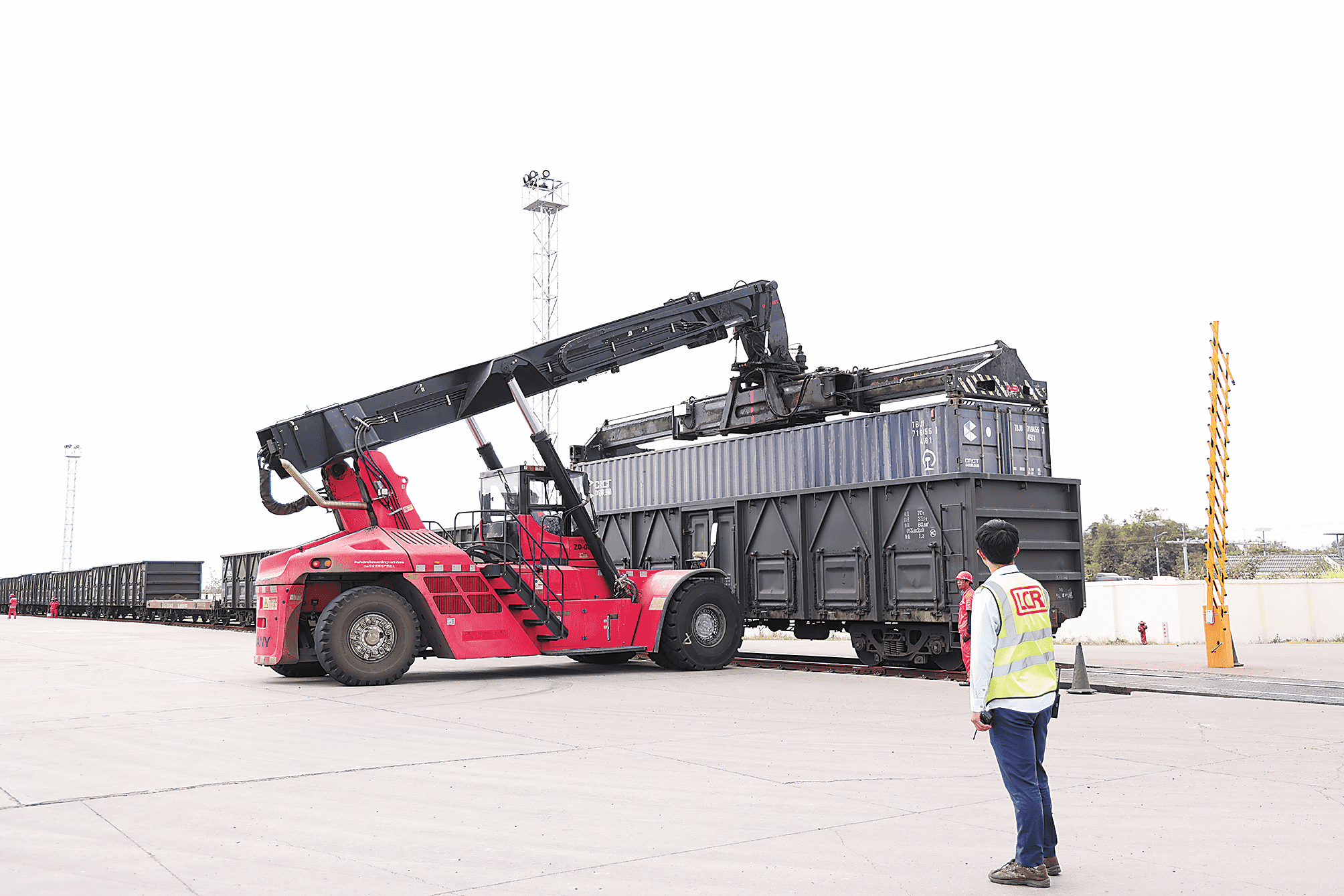
A reach stacker lifts a container at the freight yard of the Vientiane South Station of the China-Laos Railway in Vientiane, Laos. (People's Daily/Yang Yi)
Unny Sankar Ravi Sankar, minister of economic affairs of the Malaysian Embassy in China, noted that the RCEP provides abundant opportunities for businesses and investors in the region, contributing to the stable economic development of the Asia-Pacific.
Invigorating regional economic integration
In December 2024, the RCEP Support Unit (RSU) was officially established in Jakarta with the joint efforts of China, the non-ASEAN rotating chair of the RCEP that year, and the ASEAN chair Indonesia.
Kao Kim Hourn, secretary-general of ASEAN, said that the establishment of the RSU was another significant milestone in the development of the RCEP. It will help implement the RCEP in a more comprehensive and high-quality manner and provide support to relevant institutions.
Over the past three years, the RCEP has been unleashing benefits in trade, investment, and regional value chains. As the largest economy of the RCEP, China has been an active promoter of high-quality implementation of the agreement. In the first three quarters of 2024, imports and exports between China and other RCEP members totaled 9.63 trillion yuan ($1.31 trillion), a year-on-year increase of 4.5 percent.
China's continuous expansion of high-level opening up has injected stability and vitality into the economic development of the Asia-Pacific, providing tremendous opportunities for regional countries to share China's development benefits.
Data released at the Boao Forum for Asia Bangkok Roundtable in August 2024 indicated that Cambodia is expected to graduate from LDC (least developed country) status by 2028 due to the development dividends brought by the RCEP.
Cambodian Ministry of Commerce's Secretary of State and spokesperson Penn Sovicheat, said that the RCEP and bilateral free trade agreements that Cambodia signed with countries like China and South Korea greatly boosted Cambodia's trade growth.
According to statistics released by the Department of Trade Negotiations under the Ministry of Commerce of Thailand, in the first ten months of 2024, Thailand's trade with other RCEP members reached around $269.7 billion, accounting for 53.13 percent of its total trade, up 2.69 percent from a year ago.
Tang Zhimin, director of China-ASEAN Studies at the Bangkok-based Panyapiwat Institute of Management, observed that the model of pre-establishment national treatment plus a negative list for foreign investment is one of the most important achievements of the RCEP investment rules.
"Since the implementation of the RCEP three years ago, China has made significant progress in facilitating services trade and investment cooperation with ASEAN countries, demonstrating an increasingly higher level of opening up," Tang noted.
Photos
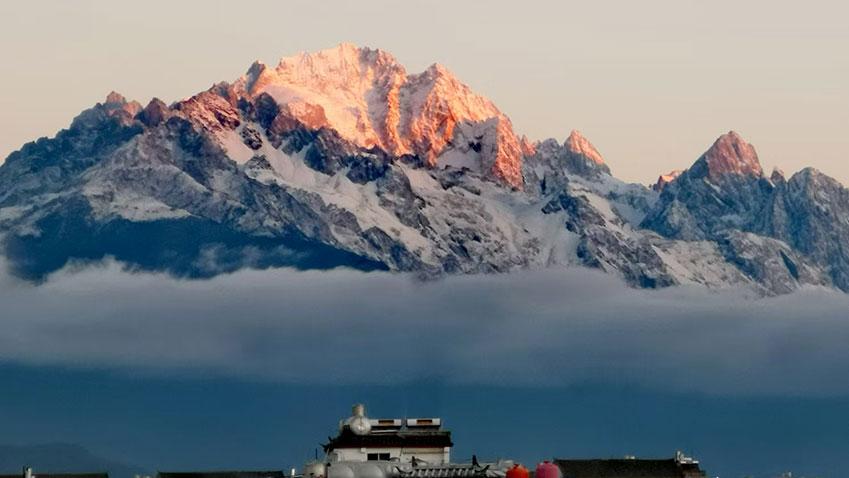 Stunning beauty of Yulong Snow Mountain after snowfall in SW China's Yunnan
Stunning beauty of Yulong Snow Mountain after snowfall in SW China's Yunnan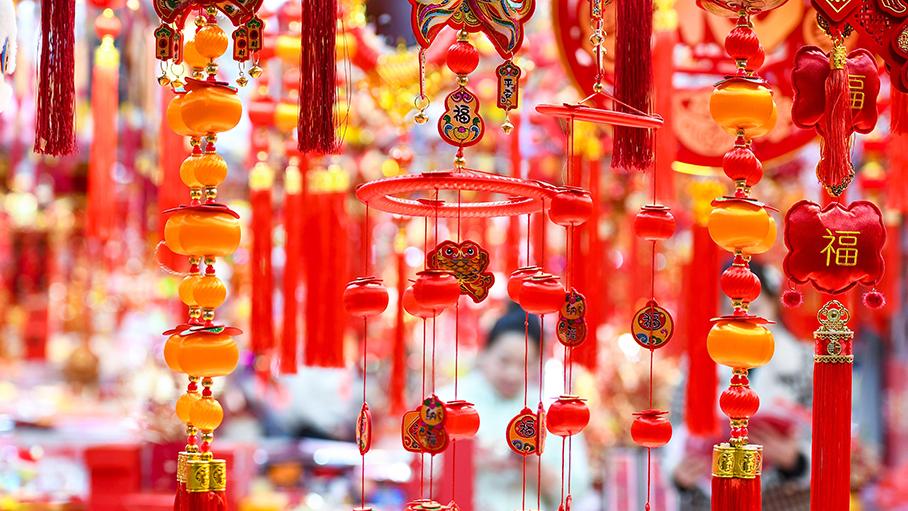 Shopping for Spring Festival goods brings festive cheer to E China's Jiangsu
Shopping for Spring Festival goods brings festive cheer to E China's Jiangsu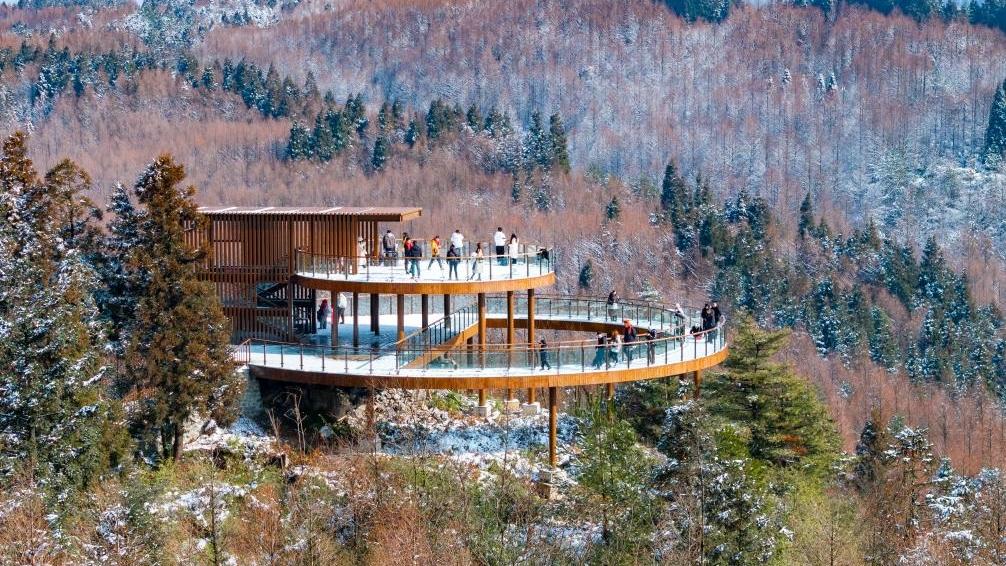 Snow scenery of Shanwangping Karst national ecological park in Chongqing
Snow scenery of Shanwangping Karst national ecological park in Chongqing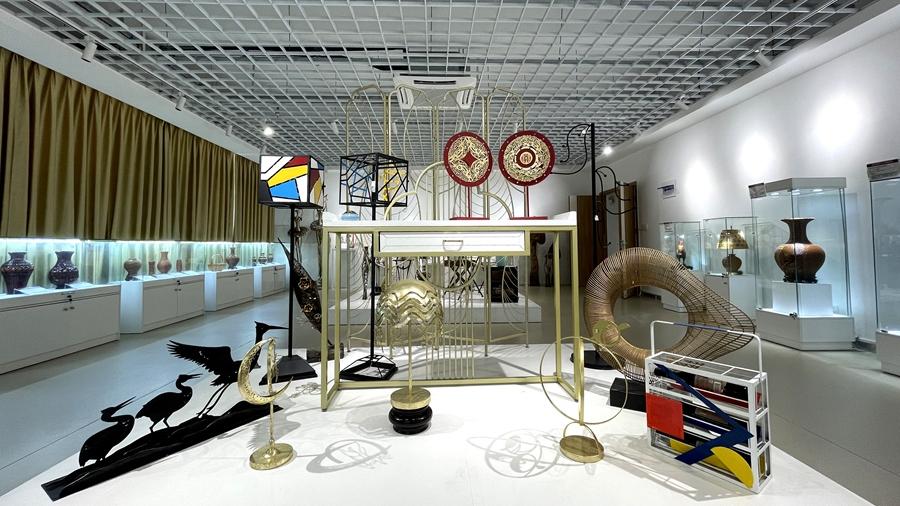 Anxi in SE China's Fujian develops rattan iron crafts into industrial chain worth over 10 bln yuan
Anxi in SE China's Fujian develops rattan iron crafts into industrial chain worth over 10 bln yuan
Related Stories
- RCEP, FTAs key to attracting FDI to Cambodia in 2024: official
- RCEP, bilateral FTAs drive Cambodia's trade growth in 2024
- China hails trade, investment achievements of RCEP at three-year mark
- China to continue quality implementation of RCEP three years on: spokesperson
- RCEP showcases success of open world economy
Copyright © 2025 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.