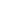China's largest desert freshwater lake becomes leading breeding ground for rare bird
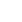
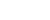
XI'AN, June 5 (Xinhua) -- Thanks to years of effective ecological management efforts, Hongjiannao Lake, China's largest desert freshwater lake, has become the world's leading breeding ground for the endangered relict gull, according to researchers in northwest China's Shaanxi Province.
Hongjiannao Lake is located in the Mu Us Desert in Shaanxi. From April to August each year, a large number of relict gulls migrate from the Bohai Bay area to breed at the lake. After the young gulls have matured, they will migrate back to their wintering grounds in July and August, according to Xiao Hong, a researcher at the Shaanxi Institute of Zoology.
With a population of around 20,000 worldwide, the relict gull is globally endangered and under first-class national protection in China.
According to Xiao, the water area of the lake has continuously expanded and the surrounding environment steadily improved in recent years. As a result, the number of relict gull nests there had increased from 2,800 in 2020 to nearly 5,000 in 2023.
This year, the number of relict gull nests at Hongjiannao Lake is up to 5,000, or 10,000 individuals, according to preliminary statistics, making it the most significant breeding base for this rare bird globally, said He Heping, director of Hongjiannao Lake National Nature Reserve Administration.
He said that since the establishment of the nature reserve administration in 2017, in collaboration with universities and research institutions, a series of specialized research projects have been conducted, including water quality assessment and feasibility studies concerning relict gull protection, providing a scientific basis for subsequent conservation efforts.
Insufficient water supply has been a longstanding challenge at Hongjiannao Lake. Since 2016, measures such as the increasing of water supply and dredging of inflow channels have been implemented. As a result, the water area of the lake has expanded from 31.5 square km in 2015 to the current 37.1 square km.
"In addition to relict gulls, Hongjiannao Lake is also a habitat for 194 other bird species, including the black stork and saker falcon," said He. "Through habitat restoration, wetland management along the shores of the lake, stocking and releasing of fish, establishment of bird identification systems and strengthening of patrol efforts, we continuously enhance the diversity and stability of the wetland ecosystem at Hongjiannao Lake, striving to provide a harmonious habitat for birds."
Photos
Related Stories
- UN chief calls for protecting Earth ahead of World Environment Day
- China concludes 232,000 first-instance environment, resources cases in 2023
- China's top procuratorate to oversee major environmental damage cases
- Chinese scientists establish bilingual air quality research data sharing platform
- China launches new round of environmental inspections
Copyright © 2024 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.