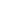China's Northwestern Polytechnical University develops AI robotic guide dog
A robotic guide dog, marking a major advance in offline embodied artificial intelligence, has been developed by a team at China’s Northwestern Polytechnical University.
Embodied AI refers to intelligent machines with a physical form that can interact with the environment in real time. Professor Li Xuelong and his team designed the robotic dog to function independently offline, enabling it to intelligently interact with humans and assist them in various situations, such as using elevators, crossing streets, and navigating indoor environments.
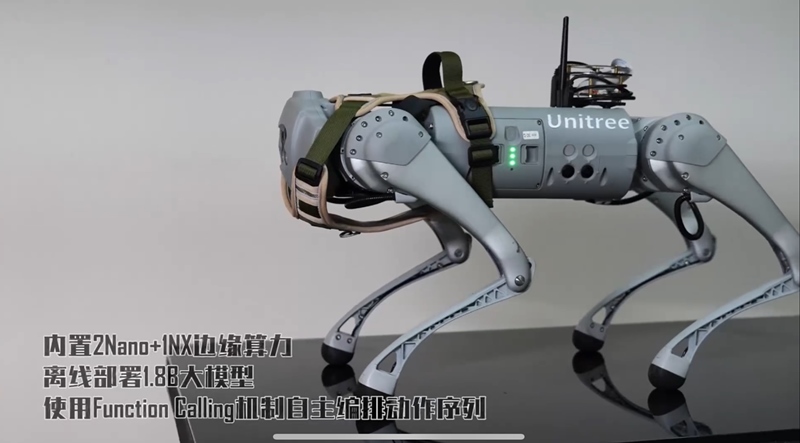

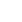
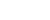
The video screenshot shows a robotic guide dog developed by Professor Li Xuelong's team at Northwestern Polytechnical University.
According to Li, the robotic guide dog demonstrates the potential of offline embodied AI as a feasible alternative to traditional guide dogs, emphasizing its ability to operate independently without internet connectivity. Moreover, it introduces an innovative solution to alleviate the shortage of guide dogs available to visually impaired individuals.
In recent years, the development of robotic guide dogs has accelerated, fueled by advancements in robotics and Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology.
However, earlier versions of these robotic guide dogs could not engage in free conversation with humans, primarily due to limitations in natural language processing technology. This shortfall also impeded their ability to provide emotional companionship.
To overcome these limitations, Professor Li's team combined the latest techniques in large-model quantization, compression, and accelerated inference. This approach enabled them to successfully deploy large models on the robotic dog's low-power computing platform, thus validating the feasibility of offline embodied AI.
The robotic guide dog has proven effective at communicating with visually impaired individuals, guiding them through various challenging environments such as roads, stairs, and elevators. Experiments conducted by the team have confirmed that the robotic guide dog can intelligently interact with humans, provide guidance in areas with weak network connectivity, and navigate indoor spaces.
Photos
Related Stories
- Humanoid robot competition in Beijing draws visitors
- Experts call for more efforts in robotics
- China develops robot for cultural relics protection
- Robots enhance services, efficiency during Spring Festival holiday in China
- Humanoid robots make public debut in Beijing
- Futuristic scene of robots taking over backbreaking farm jobs on horizon
Copyright © 2024 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.