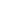New technologies enhance freshwater lake preservation

This aerial photo taken on June 1, 2023 shows the tourist dock of Baiyangdian Lake in Xiong'an New Area, north China's Hebei Province. (Xinhua/Zhu Xudong)
SHIJIAZHUANG, July 20 (Xinhua) -- Baiyangdian Lake, the most popular tourist destination in the Xiong'an New Area, gives the public a glimpse of how cutting-edge technologies support the ecological conservation of the "future city."
A water-air-ground integrated monitoring system has been put into operation to help improve water quality in Baiyangdian, the largest freshwater wetland in northern China.
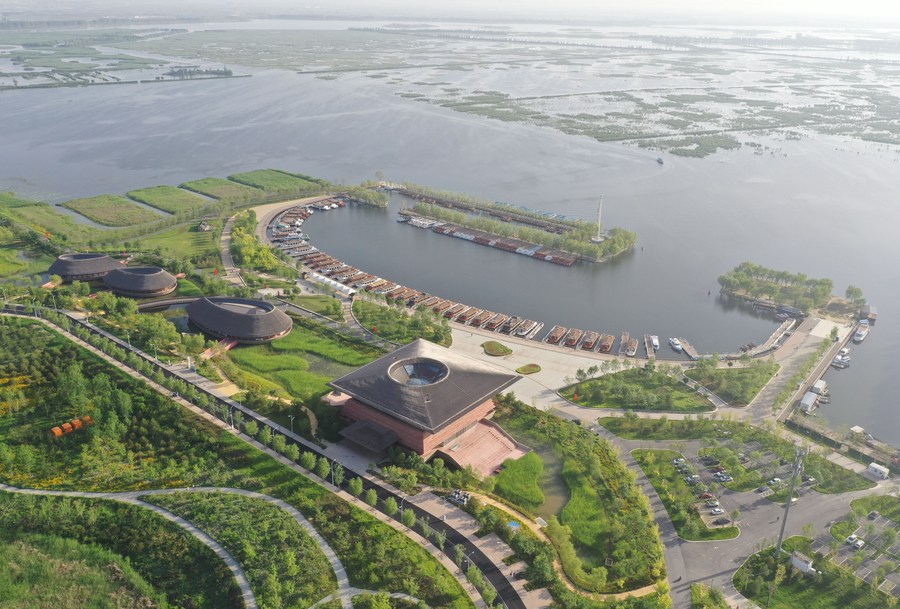
One of the tools is an unmanned ship with multiple uses. Its hull-mounted sonar equipment can monitor buried pipelines beneath the lake surface and analyze the water quality immediately after sample collection.
The carbon-fiber boat can automatically collect data about the surrounding environment in one hour, including air, dirt, and noise.
The system also features the employment of drones. The flying craft's remote sensing spectrum-imaging technology can provide a wider field of view to identify water pollution.
To strengthen observation capabilities, the lake staff have deployed both fixed devices and floating boats with real-time video feedback in the 360-square-km lake area. The 5G network's high speed and low latency, combined with virtual reality equipment, enable people to inspect the lake surface visually and obtain data in time.
According to the project manager Lin Kuntang, lake water monitoring mainly relied on human observation in the past. Since 2019, the new technology system has significantly decreased manual labor and increased work efficiency, enabling personnel to identify pollutants more quickly and accurately.
"There is no blind spot," Lin said.

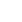
This aerial photo taken on April 7, 2023 shows vessels cruising during the trial operation of the Baiyangdian Lake water bus service in Xiong'an New Area, north China's Hebei Province. (Xinhua/Mu Yu)
Lin believes that it is worth putting huge sci-tech efforts to protect the lake.
Many Chinese folks hold a particular place in their hearts for Baiyangdian. In several famous literary works from the 1940s, the lake flourished with reed beds, towering lotus fields, and an abundant harvest from the water.
Between the 1960s and the 1980s, however, it suffered severely from industrial pollution, when sewage-carrying chemicals poisoned water and lake beds, decimating aquatic life. The lake nearly dried up in the 1990s because of climate change. After that, habitat loss and human interference caused bird numbers to decline drastically.
Hao De, a 21-year-old from a nearby village, recalled that the water quality was poor and looked dirty when he was a teenager. "My friends and I seldom went near the lake."
The lake's rehabilitation and protection activities have improved since the Xiong'an New Area was established in 2017.
Local governments strengthened their control over industrial and agricultural pollution sources by shutting down polluting firms. They also undertook efforts to replenish water supplies, allowing millions of hectares of agriculture to revert to wetlands.

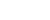
The photo taken on Nov. 5, 2022 shows an unmanned ship conducting monitoring operations on the Baiyangdian Lake, Xiong'an New Area, north China's Hebei Province.(Xinhua/Zhu Xudong)
Tech support is another significant force to drive environmental protection progress. China saw an increase in 5G-related applications in 2019, and the domestic BeiDou Navigation Satellite System continued integrating into many sectors. Technology companies and academic organizations have been pushing to develop lake monitoring devices using these new technologies.
Lin said that some of the monitoring system's designs and components have been granted patents. Researchers from Tsinghua and other universities also visited the lake to collaborate on research and development.
These efforts have paid off. The first indication of improvement was in the water quality, which rose from the lowest Grade V to Grade III by the five-tier quality standard used in the nation.
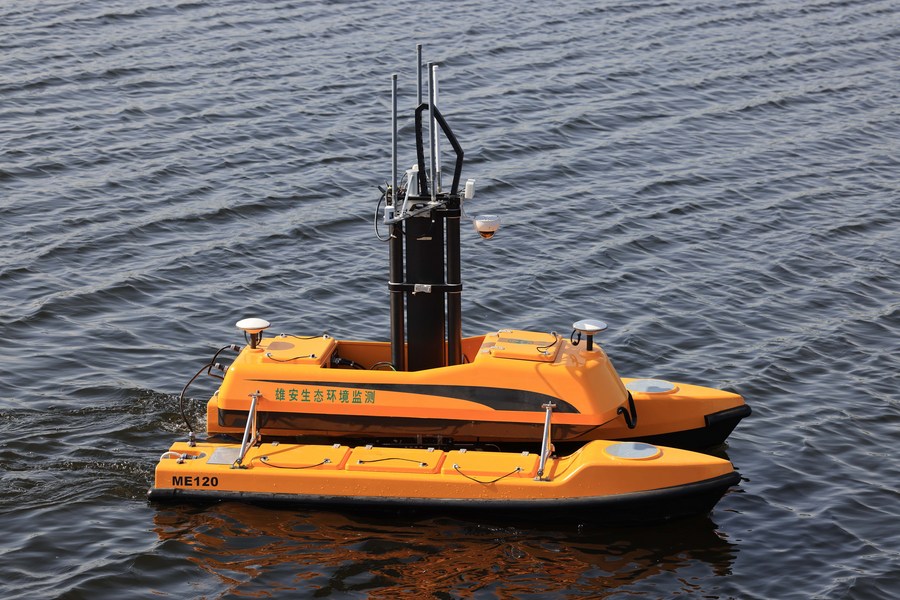
More wild creatures are returning to Baiyangdian as the water quality improves. The number of bird species in the lake area has risen to around 254, including 48 under first-rate national protection. The lake has steadily evolved into a haven for stunning lotus, blooming reeds, and a plethora of fish species.
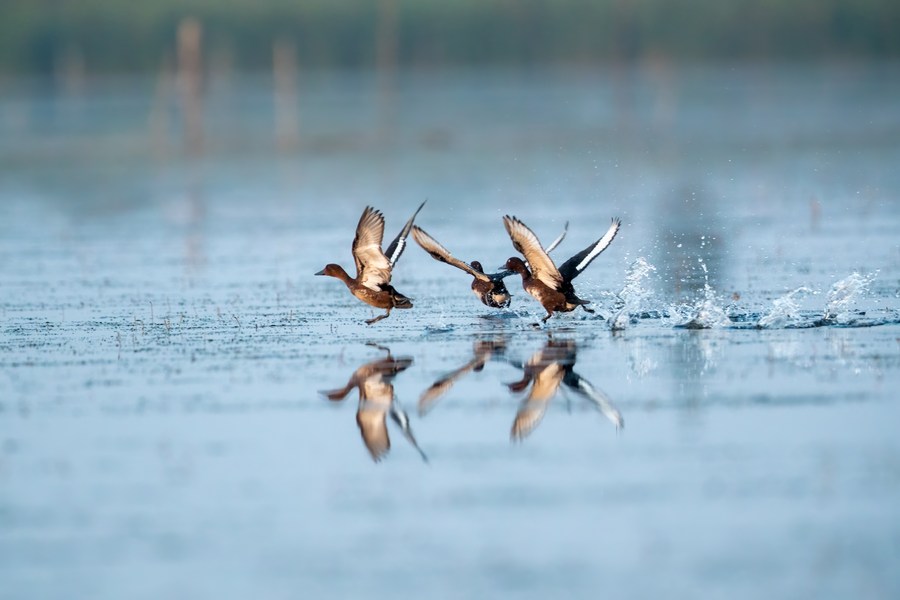

Photo taken on Sept. 9, 2022 shows wild pochards in Baiyangdian Lake in Xiong'an New Area, north China's Hebei Province. (Photo by Liu Xun/Xinhua)
However, technological advancements in environmental preservation cannot replace human efforts completely.
Ma Dongtao, a senior official of the local ecological bureau, said that residents of the lakeside villages discovered ways to reduce their waste pollution and give up their lakefront private farming. More importantly, they are more aware than ever that protecting the lake positively affects the environment and the economy.
Villagers are developing tourism. More restaurants and guest homes have opened in Xiong'an to accommodate tourists and birdwatchers.
"I was surprised to see the change since 2022," said Hao. The college student is now on summer break. "I am regular at the lake now."
Photos
Related Stories
- China a doer on ecological conservation, climate governance: spokesperson
- Historic changes in China attest to its progress on ecology
- Eco Forum Global highlights China's contribution to harmony between man, nature
- Explainer: Why green pursuit in China's mountain region matters to world
- China's concerted ecological conservation efforts yield fruitful outcomes
Copyright © 2023 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.