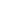Tibetan antelopes returning to natural habitats with offspring
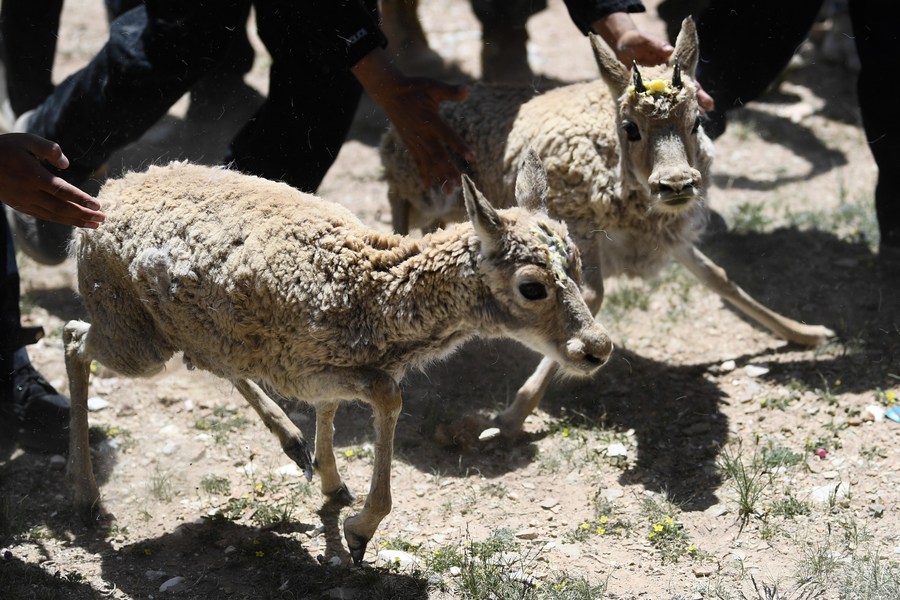

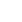
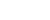
Tibetan antelopes are released into the wild at a wildlife rescue center of the Sonam Dargye Protection Station in Hoh Xil, northwest China's Qinghai Province, July 7, 2021. Tibetan antelopes are mostly found in China's Tibet Autonomous Region, Qinghai Province and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. (Xinhua/Zhang Long)
XINING, Aug. 12 (Xinhua) -- Thousands of Tibetan antelopes are returning to their natural habitats after giving birth in the heart of northwest China's Hoh Xil nature reserve, according to the reserve's management bureau.
Every year, pregnant Tibetan antelopes migrate to Zonag Lake in Hoh Xil between May and July to give birth and leave with their offspring around August.
During lake patrols this year, rangers spotted over 10,000 Tibetan antelopes give birth on the hillsides near the water body. No poaching or illegal traversing was reported.
The management bureau has put in place measures such as temporary traffic control, prohibition on honking and patrolling along the antelopes' migration routes to ensure the animals reach their breeding spots undisturbed.
"Since mid-July, rangers have spotted over 1,500 Tibetan antelopes cross the Qinghai-Tibet highway," said Phutso Tsering, head of a protection station of the bureau.
The status of Tibetan antelopes in China has been downgraded from "endangered" to "near threatened" amid the country's anti-poaching and biodiversity protection efforts, said the National Forestry and Grassland Administration.
The population of the species has grown from less than 70,000 during the 1980s-1990s to around 300,000, the administration added.
The species, mostly found in Tibet Autonomous Region, Qinghai Province and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, is under first-class state protection in China. It plays a key role in maintaining ecological balance on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Enditem
Photos
Related Stories
Copyright © 2021 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.