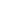China achieves remarkable results in space breeding
A group of seeds, including orchid and sealwort, a kind of traditional Chinese herb, have been taken into space for breeding tests, accompanying the three taikonauts in China’s Shenzhou-12 manned spaceship, which docked with the country’s space station core module Tianhe on June 17.
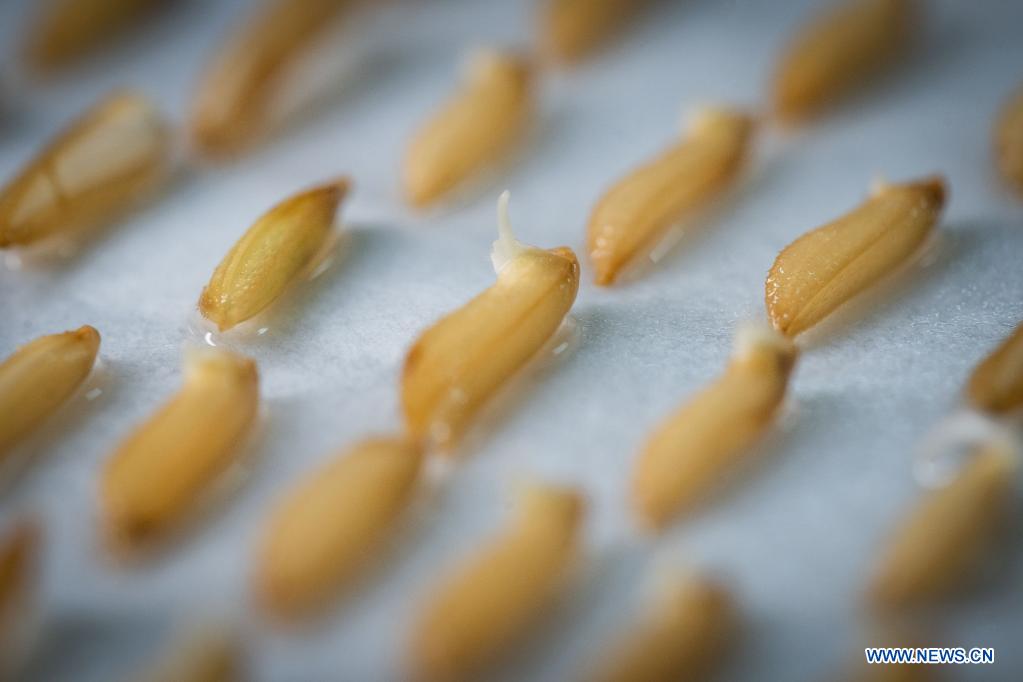

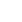
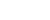
Photo taken on Feb. 26, 2021 shows sprouting rice seeds that had made a round trip to the moon aboard the Chang'e 5 probe at the central greenhouse of the National Engineering Research Center of Plant Space Breeding of the South China Agricultural University (SCAU) in Guangzhou of south China's Guangdong Province. (Xinhua/Liu Dawei)
This is China’s latest experiment in space-induced mutation breeding, which refers to the process of exposing seeds to conditions such as cosmic radiation in spaceflight, including recoverable satellites, and then sending them back to Earth for further observation and planting.
China has been carrying out space breeding for 34 years since its first space breeding experiment in 1987 with a recoverable satellite, said Zhang Yunwei, a professor at the College of Grassland Science and Technology of China Agricultural University (CAU), noting that the technique is an effective means of creating new varieties of crops.
China is a powerhouse in breeding plants in space, Zhang added, explaining that various kinds of seeds of plants, including rice, maize, wheat, rhodiola rosea, and dendrobium officinale, have been taken into space.
"As of 2018, China had bred 42 new rice varieties through space breeding. In 2006, a satellite named Shijian-8 returned to Earth carrying 215 kg of seeds ranging from grains to vegetables and fruits, the largest payload of its kind,” Zhang said.
Space breeding has helped to produce about 200 new types of mutated plants in China that have been approved for cultivation, according to Zhang.
Since 2009, the National Engineering Research Center of Plant Space Breeding of South China Agricultural University and the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) have been engaging in research and application of space breeding technology.
In 2018, 14 research institutes, including CAAS and CAU, established China’s space breeding industry innovation alliance to boost the commercialization of the technology. So far, at least 130 research institutes in the country have participated in space breeding research.
Photos
Related Stories
Copyright © 2021 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.