

Now most of the mobile phones on market have adapted to China’s homegrown Beidou Navigation Satellite System, including those of Huawei, Xiaomi, HTC, Meizu and Nubia.
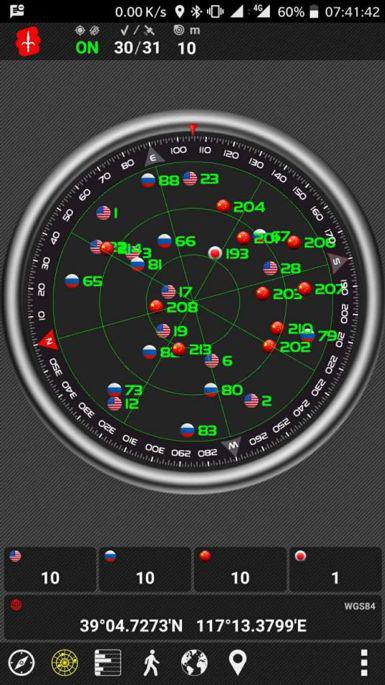
The reception of Beidou signal depends on the positioning chips of the mobile phones. At present, most of the chips simultaneously support the three major positioning systems, namely the US’s Global Positioning System (GPS), Russia's GLONASS, and China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System.
As a matter of fact, mobile phones are not the first field of application for the China-developed positioning system. China’s Ministry of Transport stipulated that all bus tour charters and vehicles carrying hazardous materials should install the Beidou system starting from the beginning of 2013.
According to Ran Chengqi, director general of the China Satellite Navigation Office and Beidou spokesperson, around 4.8 million commercial vehicles in China have been equipped with the Beidou system, making it the world’s largest collection of vehicles connected via the internet.
In addition, each local government in China has incorporated Beidou into their Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS). These stations were used to receive GPS signals, and now they have become more functional, economical and efficient.
For instance, Beijing is now home to over 20 CORS, realizing centimeter-level accuracy in positioning service.
 Fire brigade in Shanghai holds group wedding
Fire brigade in Shanghai holds group wedding Tourists enjoy ice sculptures in Datan Town, north China
Tourists enjoy ice sculptures in Datan Town, north China Sunset scenery of Dayan Pagoda in Xi'an
Sunset scenery of Dayan Pagoda in Xi'an Tourists have fun at scenic spot in Nanlong Town, NW China
Tourists have fun at scenic spot in Nanlong Town, NW China Harbin attracts tourists by making best use of ice in winter
Harbin attracts tourists by making best use of ice in winter In pics: FIS Alpine Ski Women's World Cup Slalom
In pics: FIS Alpine Ski Women's World Cup Slalom Black-necked cranes rest at reservoir in Lhunzhub County, Lhasa
Black-necked cranes rest at reservoir in Lhunzhub County, Lhasa China's FAST telescope will be available to foreign scientists in April
China's FAST telescope will be available to foreign scientists in April "She power" plays indispensable role in poverty alleviation
"She power" plays indispensable role in poverty alleviation Top 10 world news events of People's Daily in 2020
Top 10 world news events of People's Daily in 2020 Top 10 China news events of People's Daily in 2020
Top 10 China news events of People's Daily in 2020 Top 10 media buzzwords of 2020
Top 10 media buzzwords of 2020 Year-ender:10 major tourism stories of 2020
Year-ender:10 major tourism stories of 2020 No interference in Venezuelan issues
No interference in Venezuelan issues
 Biz prepares for trade spat
Biz prepares for trade spat
 Broadcasting Continent
Broadcasting Continent Australia wins Chinese CEOs as US loses
Australia wins Chinese CEOs as US loses